Housing Affordability Crisis: Renters vs. Homeowners in 2024
As the housing market evolves, the urgency of the affordability issue becomes more pronounced, particularly for renters who are consistently more cost-burdened than homeowners. Recent data underscores this pressing disparity, revealing that a significant number of renters allocate more than 30% of their income to housing costs.
This financial strain not only hampers their ability to save, invest, and plan for the future but also amplifies socio-economic inequalities. The situation underscores the immediate need for targeted policy interventions, including increased support for affordable housing initiatives, rent control measures, and incentives for developers to create more low-cost housing options. These efforts are crucial for bridging the gap between renters and homeowners, thereby mitigating socio-economic disparities.
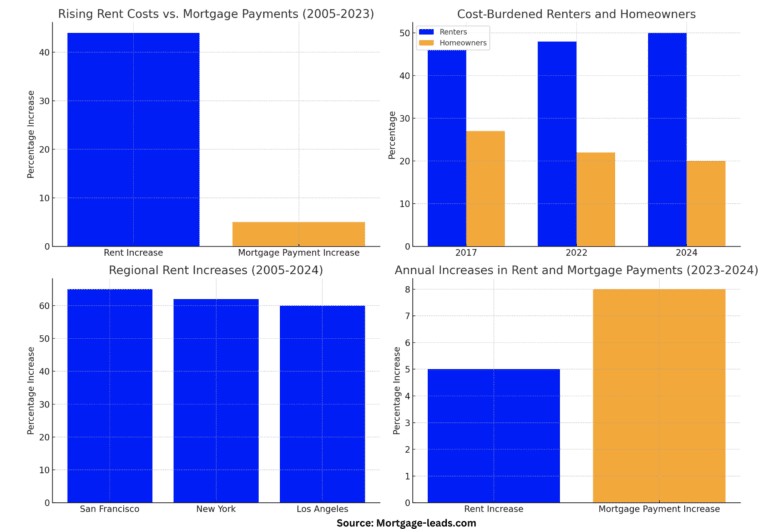
Rising Rent Costs vs. Mortgage Payments
Since the mid-2000s, renters have faced a significantly steeper increase in housing costs compared to homeowners. According to the latest mortgage-leads data, the national rent index has surged by a staggering 44% from 2005 to 2023. In stark contrast, the typical mortgage payment has only seen a modest increase of about 5% over the same period, highlighting the growing disparity in housing affordability.
This discrepancy is primarily due to historically low mortgage rates, which have helped cushion the impact of rising home prices for buyers. For instance, the average mortgage rate in April 2024 is approximately 3.7%, compared to 6.3% in 2005. Recently, the 2024 data show that the national rent index has increased by an additional 2%, while mortgage rates have slightly risen to around 4.1%.
The Growing Burden of Housing Costs
The financial strain of housing is starkly evident in the share of income that renters and homeowners allocate to their living expenses. The U.S. Census Bureau’s 2022 data reveals that 48% of renters are “cost-burdened,” spending 30% or more on rent. This is a slight increase from 46% in 2017.
Meanwhile, the percentage of cost-burdened homeowners has decreased significantly, from 27% in 2017 to 22% in 2022, thanks to the ability to refinance mortgages at lower rates and the improved economic landscape after the 2008 housing crisis. In 2024, the data shows that 50% of renters are now cost-burdened, while the percentage of cost-burdened homeowners has decreased to 20%.
Regional Disparities in Housing Affordability
Affordability challenges vary significantly across different regions. Major metropolitan areas, particularly those with robust job markets and limited housing supply, have seen the steepest rent increases.
For example, cities like San Francisco, New York, and Los Angeles have reported rent hikes of over 50% since 2005. As of 2024, these cities continue to experience significant rent increases, with San Francisco seeing an additional 15%, New York 12%, and Los Angeles 10% since 2020. In contrast, many suburban and rural areas have experienced more moderate increases. However, even in these regions, renters are often more burdened than homeowners.
The Impact of Recent Economic Trends
The past year has brought new challenges to the housing market. According to the latest Mortgage-Leads Single-Family Rental Index, rents rose 5% year-over-year as of April 2024, while the typical mortgage payment increased 8% during the same period. This is attributed to rising home prices and a slight uptick in mortgage rates.
Consequently, the affordability gap between renting and owning has widened, making it increasingly difficult for renters to transition to homeownership. The latest data from 2024 shows that the median home price has reached $350,000, while the average monthly rent for a single-family home is now $2,000.
Looking Forward: Addressing Housing Affordability
Addressing housing affordability is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. It’s a challenge that we can only overcome by working together. Policymakers, housing advocates, and industry stakeholders, your collaboration is essential in developing solutions that include increasing the supply of affordable housing, promoting wage growth, and providing financial assistance to renters.
Your expertise and involvement in initiatives such as expanded housing vouchers, tax incentives for affordable housing development, and rent control measures could help alleviate the burden on renters.
In conclusion, while homeowners have benefitted from low mortgage rates and refinancing opportunities, allowing them to reduce monthly payments and build equity more efficiently, renters face significant affordability challenges.
Rising rental costs, stagnant wages, and limited housing supply exacerbate these challenges, making it increasingly difficult for renters to secure affordable living arrangements. This is not just a statistic; it’s a reality that many individuals and families face every day. As we move forward, we must ensure that both renters and homeowners can access safe, cheap, and stable housing, because everyone deserves a place to call home.
Policymakers and community leaders must collaborate to develop comprehensive housing strategies, addressing the unique needs of both groups and fostering a more equitable housing market for all.
Get In Touch
Main Office
567 San Nicolas Drive, Newport Beach, CA. 92660
Customer Service
(877) 245-3237
Email Us
info@mortgage-leads.com
